Abstract
Background:
Venous thromboembolism (VTE) is associated with significant morbidity, functional disability and mortality which leads to annual direct medical costs of 6 to 8 billion U.S. dollars. The incidence of VTE among patients with sickle cell disease (SCD) is significantly higher than in those without SCD, with lifetime risk of up to 25%. The highly variable clinical phenotypes of SCD, in addition to complex pathogenesis of thrombosis in SCD, are challenges to the early identification of high-risk patients and timely initiation of anticoagulant prophylaxis.
Objective:
To develop a population-based risk assessment model (Predictive AlgoRithm of VTE in SCD, PARViS) for the identification of SCD patients at high-risk of VTE using least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) methodology and compare its validity to the Caprini VTE risk assessment model.
Method:
We conducted a retrospective cohort study using the 2009-2014 Truven Health MarketScan® databases to identify commercially-insured health plan enrollees with VTE and SCD based on International Classification of Diseases (ICD) codes for inpatient and outpatient encounters. Baseline characteristics were assessed over the 6 months period following cohort entry and a risk window for any VTE events starting from day 181 after cohort entry and onwards. The clinical outcomes were defined as occurrence of VTE over the 30-, 90- and 180-day period.
The population-based cohort was divided into derivation and validation sets in a 2:1 ratio. The risk score was calculated using LASSO generalized linear regression models and divided into three risk categories for predicting 180-day VTE risk. Kaplan-Meier survivor functions were estimated for VTE rates by estimated risk score and censored for end of continuous enrollment, and end of observation period. The C-statistic was used to assess the prediction performance of the 7-factor risk score, which was compared with the Caprini VTE risk prediction model.
Results:
Among 11,774 subjects with SCD in the derivation cohort, the mean (SD) age at enrollment was 32.1 (19.8) years and 62.2% were female. From the validation cohort, 5949 SCD subjects were analyzed, participants' mean (SD) age at enrollment was 32.2 (19.7) years, and 62.6% were female. The 30-, 90- and 180-day VTE rates of the overall cohort were 0.6%, 1.3% and 2.0%, respectively.
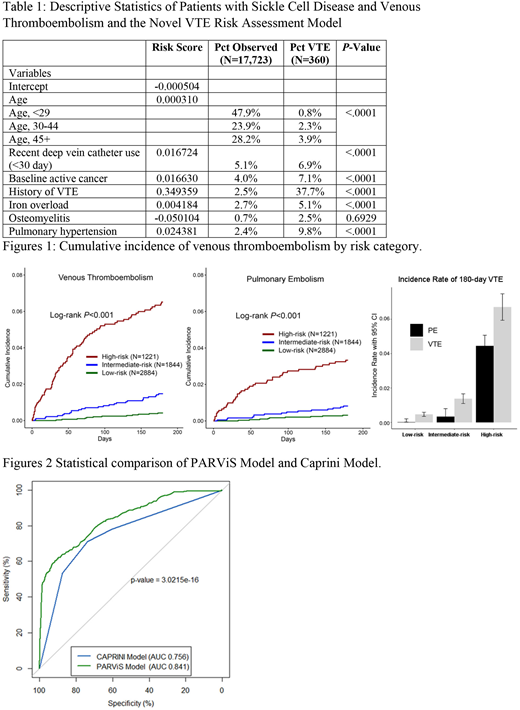
The risk model included age, recent central vein catheter use (<30 day), active cancer, history of VTE, iron overload, osteomyelitis and pulmonary hypertension. Patients with SCD in the validation cohort were stratified into high-, intermediate- and low-risk in 2:3:5 ratio by VTE risk scores. Demographics and distribution of VTE risk factors are listed in Table 1. The rates of VTE at 180-days were 0.47% (95%CI 0.35%-0.64%), 1.38% (95%CI 1.10%-1.73%),6.71% (95%CI 5.94%-7.57%). [Figure 1]
In the derivation cohort, C statistics were 0.845 (95%CI 0.818-0.872) for 7-factor RAM in predicting 180-day VTE, 0.883 (95%CI 0.853-0.914) for 90-day VTE, and 0.917 (95%CI 0.875-0.959) for 30-day VTE. In the validation cohort, C statistics were 0.833 (95%CI 0.791-0.875) for 7-factor VTE risk assessment model in predicting 180-day VTE, 0.877 (95%CI 0.831-0.923) for 90-day VTE, and 0.942 (95%CI 0.911-0.972) for 30-day VTE. Using the Caprini VTE risk prediction model, we found statistically significant differences (p<0.0001) with C-statistics for 180-, 90- and 30-day VTE prediction of 0.721 (95%CI 0.672-0.770), 0.775 (95%CI 0.719-0.830), and 0.826 (95%CI 0.759-0.892). [Figure 2]
Conclusion:
We developed and validated a 7-factor VTE risk assessment model specific to patients with SCD (PARViS). With its straightforward calculation and demonstrated accurate prediction of 6-month VTE rates in patients with SCD, the PARViS model can prove to be a useful prediction tool for clinical practitioners.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.